Microplastics Footprint
10. June 2021
STOP Microplastics Pollution! Innovation Forum
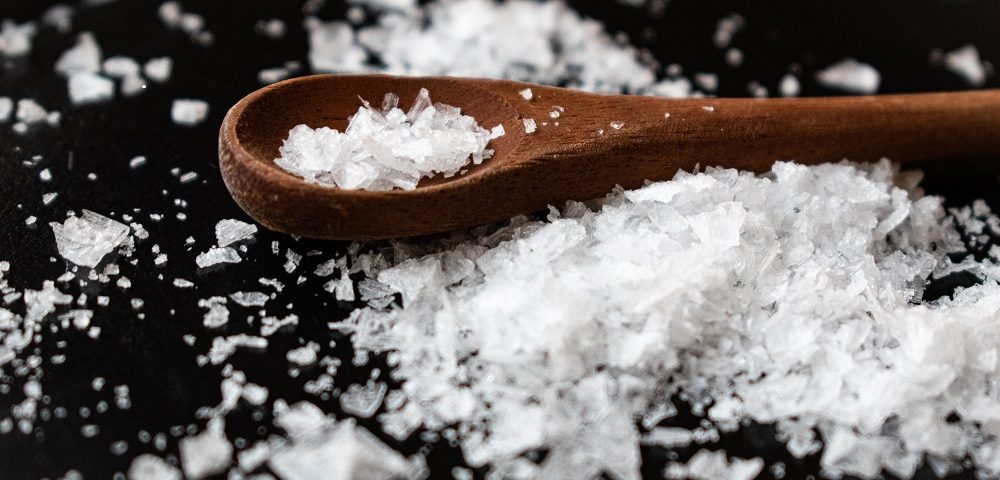
29. July 2021Microplastics in sea salt
: Why it is in there, and how to get it outMicroplastics in sea salt
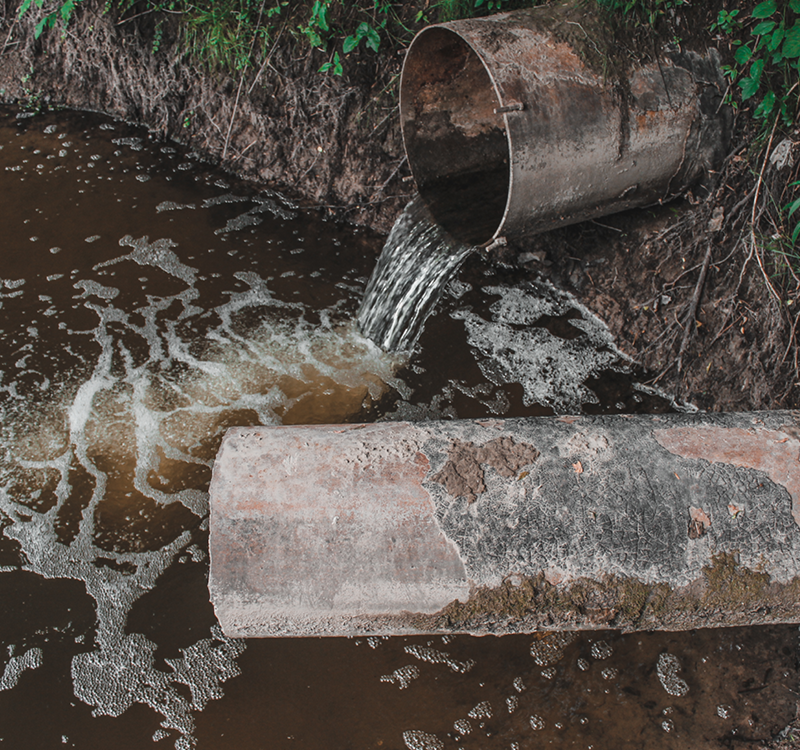
is unsurprising given the extent ofplastics littering our oceans
. Recently, we had the opportunity to take a closer look at themicroplastics pollution of sea salt produced on Java
and the methods used to do so. So this blog post is about howmicroplastics end up on our plates with sea salt
, what that means for our health, and howmicroplastic-free sea salt
can be produced.Sea Salt & Microplastics
Studies have detected
Studies have detected
microplastics in a wide variety of concentrations in sea salt products worldwide
. If you consider the garbage patches and the countless tons of plastic waste that break down into smaller and smaller particles in the sea and take centuries to decompose completely, this is hardly surprising.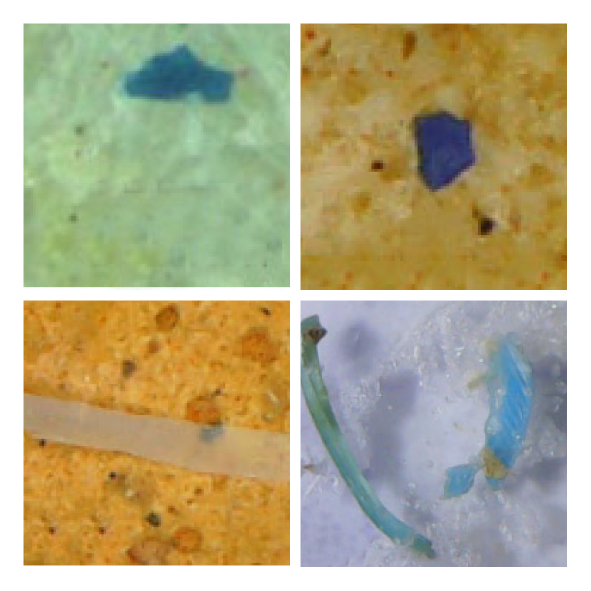
With the sea salt directly on our plate
If
Too little data, does not mean harmless
How harmful it is for humans, there is still little evidence. Even though most of the ingested microplastics are probably excreted through the digestive tract, it is known that microplastics are absorbed by human tissue. It is distributed throughout the body via the blood.
If
sea salt is used as table salt
,microplastics are transferred directly
to humans. Depending on how much (sea) salt you take in daily and throughout your life through different foods (the WHO recommends no more than 5mg daily), you may end up with quite a bit of microplastics.Too little data, does not mean harmless
How harmful it is for humans, there is still little evidence. Even though most of the ingested microplastics are probably excreted through the digestive tract, it is known that microplastics are absorbed by human tissue. It is distributed throughout the body via the blood.
The fact that microplastics serve as excellent carriers for other - provably very harmful to health - micropollutants such as heavy metals, pesticides, plasticizers and flame retardants, and also penetrate the blood-brain barrier in the nano range, makes us feel a great need to stop the further spread of microplastics in our environment and food chain as quickly and impactful as possible.
How
In a nutshell, sea salt production involves the pumping of salty seawater into large basins. It evaporates due to solar radiation and wind. What remains is the dissolved salt - and microplastics. You can see exactly how this works in the video of the (German) "Sendung mit der Maus" here.
microplastics get into sea salt
In a nutshell, sea salt production involves the pumping of salty seawater into large basins. It evaporates due to solar radiation and wind. What remains is the dissolved salt - and microplastics. You can see exactly how this works in the video of the (German) "Sendung mit der Maus" here.
What we found
As part of our collaborative study with the Indonesian Research and Development Center for Marine and Fisheries Product Processing and Biotechnology, we analyzed
The result in a nutshell: In our study, sea salt from traditional production has the highest microplastics load. Why? This is mainly due to the use of geomembranes. This prevents the saline water from seeping into the soil (like it does with the traditional method), whereby the salt dissolved in the water is lost, but the microplastics as solids do not seep. As a result, more microplastics remain in relation to the salt recovered and contamination is increased.
As part of our collaborative study with the Indonesian Research and Development Center for Marine and Fisheries Product Processing and Biotechnology, we analyzed
microplastic concentrations in sea salts
. Here, we investigated the influence of different production methods on microplastic contamination. On Java, the traditional, geomembrane and tunnel methods are used. We have described how these are constructed and work in this (German) article in Analytik News. There you also find the other figures, data and facts from our study.The result in a nutshell: In our study, sea salt from traditional production has the highest microplastics load. Why? This is mainly due to the use of geomembranes. This prevents the saline water from seeping into the soil (like it does with the traditional method), whereby the salt dissolved in the water is lost, but the microplastics as solids do not seep. As a result, more microplastics remain in relation to the salt recovered and contamination is increased.
Is microplastic-free sea salt possible?
We say yes. To completely avoid contamination of sea salt, our approach is to remove microplastics from sea water before it flows into the salt pans.
To do this, especially in such rural areas as the salterns studied in Indonesia, a cheap and technically easy-to-use method is needed. Here, Wasser 3.0 PE-X® is a promising option.
Our Solar Impulse Efficient Solution Label awarded modular low-tech plant can be placed, for example, at the inflow channels to salt pans shared by several salt producers. This enables a microplastic-free production.
We say yes. To completely avoid contamination of sea salt, our approach is to remove microplastics from sea water before it flows into the salt pans.
To do this, especially in such rural areas as the salterns studied in Indonesia, a cheap and technically easy-to-use method is needed. Here, Wasser 3.0 PE-X® is a promising option.
Our Solar Impulse Efficient Solution Label awarded modular low-tech plant can be placed, for example, at the inflow channels to salt pans shared by several salt producers. This enables a microplastic-free production.
Can Wasser 3.0 also remove all the microplastics from our oceans?
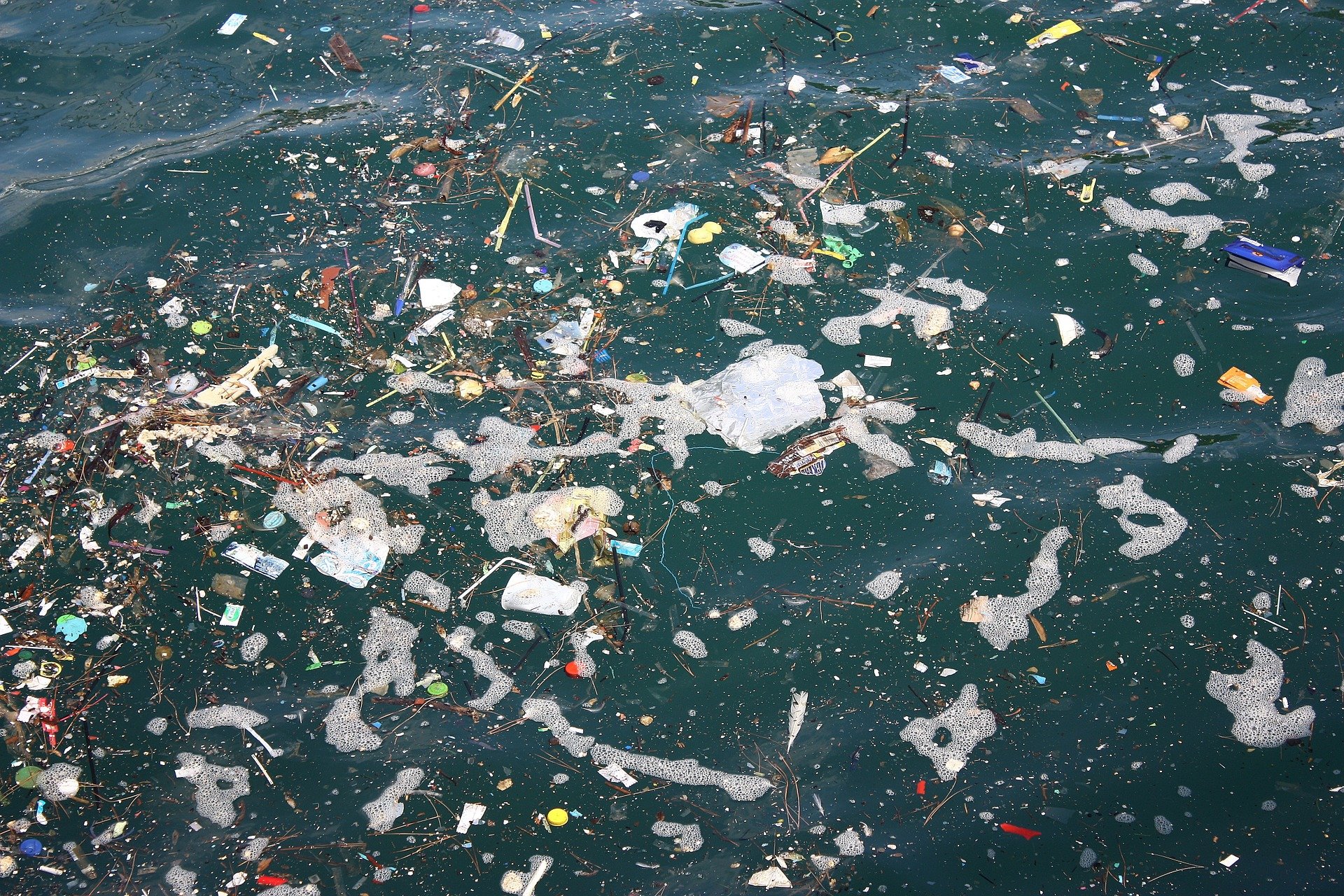

This is a question we are often asked. We see it like this: The proven, constantly growing garbage patches and other littering result in enormous amounts of microplastics for the ocean and its inhabitants. But the dimensions of our oceans are huge and the microplastics are extremely distributed.
The
According to our findings,
The
removal of microplastics from seawater
therefore makes sense in places that form somehow contained systems with high loads, and where the benefits of low microplastic loads for humans, animals and ecosystems are big. Examples would be aquacultures, docks, estuaries, shipping channels, the sea salt productions described in this article, and seawater desalination.According to our findings,
seawater desalination
is particularly suitable for the use of Wasser 3.0 PE-X®. Both themaintenance of the desalination plants
and theuse of chemicals
are significantly reduced as a result. Likewise, the water thus obtained for use inagriculture
is microplastic-free.But ! To protect our
oceans from further microplastics
, it is crucial to change our global waste management so that theoceans are no longer understood and used as landfills and sewage treatment plants
.Do you have suggestions for us, have encountered an error or have a question? Please feel free to get in touch with us.







